The American Dental Association estimates that periodontal disease affects nearly half of Americans over the age of 30. Also known as gum disease, periodontal disease causes inflammation of the tissues supporting and holding the teeth in place.
One of the rare oral care procedures that can reverse the effects of gum disease is gingivectomy.
Gingivectomy is used to treat gum disease when root planing and scaling are no longer effective. This procedure treats the consequences of periodontal disease or addresses a gum problem that affects the teeth’ supporting structures.
Read on to find out more about this oral surgery procedure.
What Is a Gingivectomy?
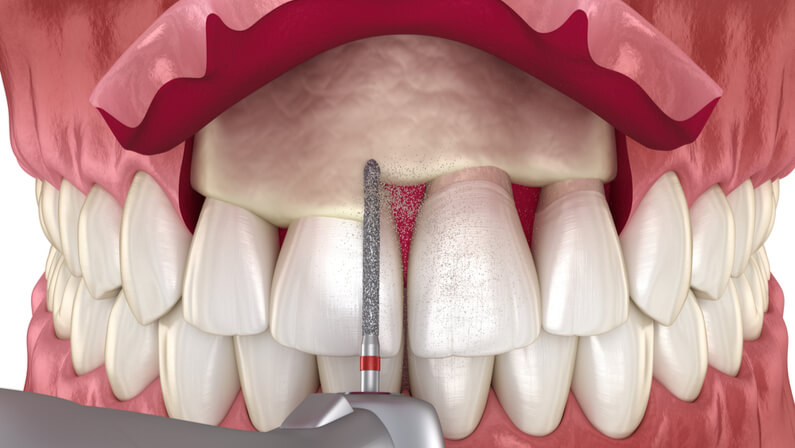
A gingivectomy, also known as crown lengthening, is a form of oral surgery that involves removing gums in a minimally invasive to moderately invasive manner. The technique controls tissue overgrowth and improves the appearance of teeth by removing the gingiva.
The majority of people get gingivectomies only when they become adults. A gingivectomy is the best treatment option to make your smile look as it should.
This holds if you’ve taken drugs (such as some forms of blood pressure pills) or undergone hormonal changes (such as pregnancy gingivitis) that cause your gums to become bigger and look unnatural.
Others discuss obtaining one with their dentist as they have a gummy smile that causes their teeth to appear short.
Getting a gingivectomy instead of a more expensive aesthetic procedure is a less intrusive and more cost-effective option. As long as the procedure is done with a laser, you should notice spectacular effects the same day.
Candidate for gingivectomy
A dentist may recommend gingivectomy for those experiencing a gum recession as a result of:
- gum injury
- gum injury infections caused by bacteria
- Gingivitis
- aging
A dentist may offer a gingivectomy to anyone with gum disease to prevent further damage. It also makes it easier for your dentist to clean your teeth.
Gum disease frequently results in holes at the base of the teeth. These gaps can lead to the accumulation of:
- Calculus
- tartar
- bacteria
- plaque
Further damage can result from these buildups.
If your dentist discovers an infection or gum disease during a cleaning or dental care check-up and wants to stop it from progressing, he or she may propose this operation.
Gingivectomy Procedure

A gingivectomy takes between 30 minutes to one hour, depending on the amount of gum tissue removed by your dentist.
Minor operations involving one tooth or a few teeth will most likely just require one appointment. Major gum contouring or removal may need multiple visits— particularly if your dentist wishes to let one area heal before moving on to the next.
The following is how the procedure works:
- To numb the area, the dentist injects a local anesthetic into the gums.
- The dentist performs a soft tissue incision using a laser tool or a scalpel to cut away sections of gum tissue.
- During the process, your dentist will most likely use a suction tool to remove extra saliva from your mouth.
- The dentist may use a laser tool to vaporize excess tissue and sculpt the gumline after the tissue has been taken away.
- As you heal, your dentist applies a soft dough-like substance and bandages to the area for gum protection.
How do scalpel and laser procedures compare?
Gingivectomy can be done in a number of ways, but the most common ones are with a scalpel or a laser. For many years, small surgical blades and other periodontal surgical instruments were used to cut the tissue and move the gingival margin into a better position during a gingivectomy.
Scalpel is easy to use, cuts cleanly with clear edges, wounds heal quickly, and there is no damage to the surrounding tissue. Scalpels have some drawbacks, like the need for anesthesia, bleeding that makes it hard to see, and the fact that the cut isn’t sterilized.
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation is what LASER stands for. Whether to do a traditional gingivectomy with a scalpel or a laser gingivectomy depends on a lot of different things.
In one study, they compared the two methods. First of all, with laser gingivectomy, the surgery was easier and took less time than with traditional gingivectomy.
In the traditional gingivectomy, there was bleeding, but there was less blood in the laser procedure. With laser gingivectomy, you need less anesthesia.
In laser gingivectomy, the pain after the surgery was less than in conventional gingivectomy. This could be because the heat from the laser shuts down the pain receptors, and the coagulation process makes the wound dry and less likely to get infected.
What To Expect After Surgery
You may have bleeding and swelling, as well as chapped lips or bruising, following your gingivectomy. You should use an ice pack every 15 minutes during the first two days to help with swelling. After the third day, you can use a heat pack every 20 minutes. Keeping your head raised will also help reduce swelling.
For the first 48 hours post-surgery, you may notice that your saliva appears pink. You should avoid eating hot meals and rinse your mouth to reduce bleeding. The bleeding will continue if you eat hot foods or rinse your mouth.
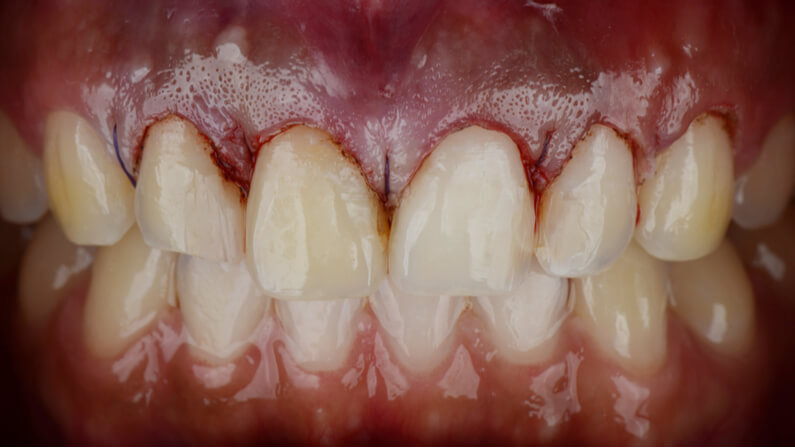
Gingivectomy Recovery and Healing Time
Most people recover quickly from a gingivectomy. Here’s what to anticipate.
The First Few Hours
You shouldn’t have to wait to go home. Most of the time, your dentist will only use local anesthesia, so you should be able to drive yourself home.
You might not feel pain right away, but as the anesthesia wears off a few hours after the procedure, the pain might get worse or last longer. Pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) that you can buy without a prescription may help.
Your gums may bleed for a few days as well. Change any bandages or dressings until the bleeding stops or your dentist says you can show your gums again.
Before sending you home, your dentist or a dental assistant should show you how to change your bandages or dressings. If they didn’t tell you how to do it or if you’re not sure what to do, call their office and ask.
The Next Few Days
You might have pain in your jaw. Your dentist will probably tell you to only eat soft foods while your gums are healing so that you don’t hurt or irritate them.
If pain or irritation in your cheeks makes its way into your mouth, try putting a cold compress on them.
Long-Term
After about a week, the pain and soreness will go away. Go back to the dentist to make sure the area is healing well and that you can go back to eating normally.
Lastly, keep your teeth in good shape. Don’t smoke, brush and floss your teeth twice a day, and eat less sugary foods.
How much does gingivectomy cost?
The price of a gingivectomy may vary.
The skilled team at Brownstone Dental is well known for providing the best dental care to the whole Houston community. For the entire family, we provide great dental care as well as a low cost of support.
Contact us right away to receive a more thorough pricing breakdown for your gingivectomy!
How do gingivectomy and gingivoplasty compare?
Gum tissue is removed during both operations. A gingivectomy removes diseased gum tissue that is around a gum pocket, whereas a gingivoplasty is performed to restructure gum tissue, typically for cosmetic purposes.
This is the fundamental distinction between the two surgeries. Gingivectomy and gingivoplasty can be combined, and in some circumstances, a gingivectomy can be used for cosmetic operations.
When to See a Dentist
If you think you might benefit from a gingivectomy, talk to your dentist. Some people receive a gingivectomy following braces only when advised by their orthodontist. Dental professionals can inform you if the operation is right for you and explain the benefits and drawbacks.
The most important advantage of a gingivectomy is that it improves your oral health. Preventative care check-ups are, of course, your best bet for avoiding these operations. Your dentist will be able to detect any potential problems early on, potentially preventing you from getting gum disease.
Why Might You Need a Gingivectomy?
There are several factors to consider a gingivectomy. This procedure entails reshaping inflamed gums and can be used to cure a variety of issues ranging from gum disease to merely cosmetic reasons.
Gum disease often necessitates a gingivectomy. Gingivitis can result in “pockets” between the gums and the teeth. Bacteria thrive in these pockets, irritating your gums even more. Thes.
Gum reshaping is sometimes required as part of a restoration process. When the gums obstruct access to teeth that require restoration, our experts will remove portions of the gums to provide access to the teeth in concern.
Brownstone Dental will assist you with whatever reason you require a gingivectomy. Make an appointment with one of our dentists now.