Did you know that nearly half of American adults aged 30 and older suffer from some form of periodontal disease? Periodontitis, a serious gum infection, affects millions of people worldwide. It can lead to severe complications, including tooth loss and bone damage, if left untreated. But what exactly causes periodontitis, and how can it be prevented? In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, stages, and treatments for this common condition, as well as offer advice from an expert in the field.
What Is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a severe infection of the gums that damages the soft tissue and, without treatment, can destroy the bone supporting the teeth. Healthy gums fit snugly around your teeth, providing vital support and preventing infection. However, poor oral hygiene allows plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, to build up on your teeth at the gum line. If left unchecked, this plaque hardens into tartar (calculus), which irritates the gums and triggers inflammation. This early stage of gum disease, called gingivitis, is characterized by red, swollen, and potentially bleeding gums.
It is a progressive disease that typically starts with mild gum inflammation, known as gingivitis, and worsens over time. This condition affects not just the gums but the entire structure around the teeth, including ligaments and bones.
Periodontitis is considered a major cause of tooth loss in adults. The earlier it’s identified and treated, the better the chances of controlling its progression and preventing permanent damage.
What Are The Symptoms of Periodontitis?
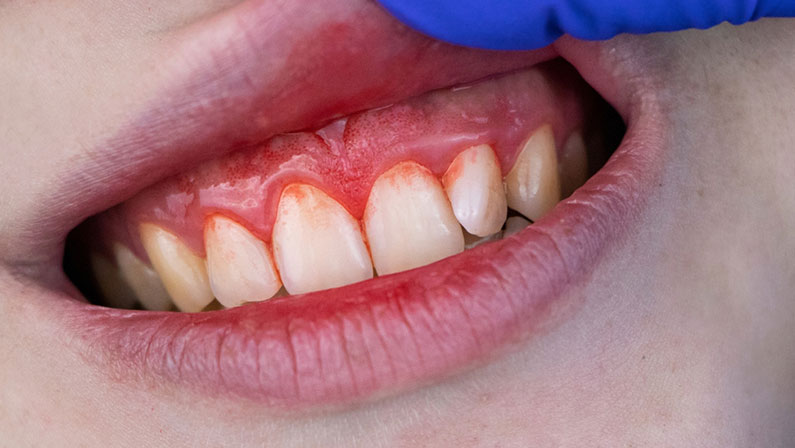
The symptoms of periodontitis can vary depending on the stage of the disease. While early stages of gum disease might not show any noticeable symptoms, periodontitis often presents with several telltale signs. Here are some key symptoms to watch for:
- Swollen, tender, or bleeding gums
- Receding gums, which make teeth appear longer
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain when chewing
- Pus between teeth and gums
If you notice any of these symptoms of periodontitis, it’s essential to visit a dentist immediately for an evaluation and treatment plan.
What Causes Periodontitis?
The primary cause of periodontitis is the accumulation of plaque on teeth. Plaque is a sticky film composed of bacteria that forms on the surface of teeth and gums. When not removed by regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, which is much more difficult to remove. Tartar harbors harmful bacteria that attack the gums and the underlying bone structure.
But what bacteria causes periodontitis?
Several types of bacteria contribute to periodontitis, but some of the most common culprits include Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola, and Tannerella forsythia. These bacteria thrive in the plaque environment and produce toxins that irritate the gums and trigger the inflammatory response. Other contributing factors also include smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and underlying health conditions such as diabetes.
What Happens if Periodontal Disease Goes Untreated?
If left untreated, periodontitis can have severe consequences, including:
Tooth loss
As the disease destroys the bone and ligaments supporting teeth, they may become loose and eventually fall out or require extraction.
Gum recession
The gums pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots and making the teeth more sensitive to temperature and prone to decay.
Bone damage
Periodontitis can lead to the loss of jawbone, which impacts the overall structure of the face and makes tooth replacement more difficult.
Systemic health issues
Research suggests that periodontitis is linked to other serious conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and respiratory problems due to the spread of harmful bacteria through the bloodstream.
What Are The Stages of Periodontitis?
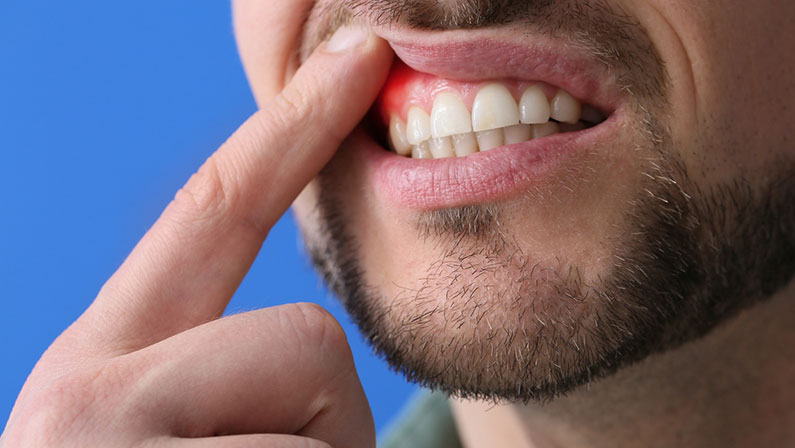

Periodontitis progresses through several stages, each with its own symptoms and severity. Understanding these stages can help in identifying the condition early and seeking timely treatment.
Inflammation (Gingivitis)
The first stage of periodontal disease is gingivitis, which is characterized by inflamed gums that may bleed when brushing or flossing. At this stage, there is no bone or tissue damage, and the disease is entirely reversible with proper oral care.
Mild Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it progresses to mild periodontitis. At this stage, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that trap plaque and bacteria. Bone loss may also start, but it is still relatively minor.
Moderate Periodontitis
In moderate periodontitis, the pockets between the gums and teeth deepen, and significant bone loss occurs. The infection spreads deeper into the gums, leading to more noticeable symptoms like bad breath, increased gum bleeding, and slight tooth mobility.
Severe Periodontitis
Severe periodontitis is the most advanced stage of the disease. It is characterized by deep pockets, extensive bone loss, loose teeth, and even abscess formation. In this stage, the risk of tooth loss is high, and the damage to the bone and gums can be irreversible without significant intervention.
How Is Periodontitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing periodontitis typically involves a thorough dental examination, during which a dentist will check for signs of gum inflammation, receding gums, and pocket depth around the teeth. X-rays may also be taken to assess bone loss, and sometimes a dental professional will use a probe to measure the space between your teeth and gums. A depth of more than 3 millimeters can indicate periodontitis.
What Are The Complications of Periodontitis?
Periodontitis, when left untreated, can lead to complications that go beyond dental health. Some of these complications include:
- Tooth loss due to extensive bone damage.
- Systemic infections caused by the spread of oral bacteria through the bloodstream.
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes.
- Respiratory infections due to bacteria entering the lungs.
- Poor diabetes control, as inflammation from periodontal disease can complicate blood sugar management.
How Is Periodontitis Treated?
The treatment for periodontitis focuses on controlling the infection, preventing further damage, and restoring gum and bone health. The approach to treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for managing periodontitis. Regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria that contribute to gum inflammation.
Professional Cleaning
For more advanced cases, professional cleaning may be necessary. This can involve scaling and root planing, a deep-cleaning method that removes tartar from below the gum line and smooths the tooth roots to promote healing.
Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate bacterial infections in the gums. These can be applied directly to the gums or taken orally.
Surgery
For severe periodontitis, surgical intervention may be required. Procedures such as flap surgery or bone grafting can help repair the damage caused by the disease, restoring the structure of the gums and bone.
Is Periodontitis Curable?
While periodontitis cannot be fully cured, it can be managed with proper treatment and ongoing oral care. Early intervention is critical in halting the progression of the disease and preventing further damage. By following a treatment plan and practicing excellent oral hygiene, individuals with periodontitis can lead a healthy, pain-free life.
How Can I Prevent Periodontal Diseases?

Preventing periodontal diseases is all about maintaining a consistent oral hygiene routine and visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups. Here’s how you can minimize your risk:
Good Oral Care
Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can go a long way in preventing plaque buildup, which is the leading cause of periodontitis.
Regular Dental Visits
Routine dental cleanings and exams are essential for identifying gum disease in its early stages and addressing any issues before they worsen. Your dentist can recommend additional preventative measures if necessary.
When Should I See A Dentist?
If you notice any symptoms of periodontitis, such as swollen, bleeding gums or persistent bad breath, it’s essential to consult a dentist as soon as possible. If you need to take time off work or school to visit the dentist, you can request an online medical certificate from a registered doctor. Early detection is key to preventing further complications, and your dentist can provide personalized advice on managing your gum health.
Prioritize Your Gum Health with Dr. Saif Shere
Periodontitis is a serious condition that can lead to long-term damage if left untreated. Fortunately, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the disease can be managed effectively.
If you’re experiencing any signs of gum disease, or simply want to maintain optimal oral health, it’s crucial to seek professional care. Dr. Saif Shere, a renowned cosmetic dentist in Houston, specializes in both cosmetic and preventive dental services. Located at 9824 Fondren Rd, Houston, TX 77096, Dr. Shere and his team at Brownstone Dental offer a range of treatments designed to address gum disease and promote lifelong dental health. For more information, visit their website at Brownstone Dental, or book an appointment today to prioritize your oral well-being.